Methane Testing | The Science, Safety and Systems
LADBS Methane Tests are a field study that a licensed LADBS testing laboratory completes under the LADBS Methane Testing standards. In fact, the purpose of a methane test is to establish the methane hazardous classification level in accordance with the LADBS Methane Mitigation Standard Plans Methane Mitigation requirements. The Methane Mitigation requirements are available within the Methane Mitigation Design. Consequently, the owner will build the Methane Mitigation Construction led by a Methane Mitigation Contractor. Ultimately, the Methane Test results will drive the methane mitigation requirements.
A professional engineer or geologist must supervise methane soil gas tests. Ultimately, the LADBS Methane Soil Gas certificate of compliance will require the stamp of the supervising professional engineer. Updated January 3, 2023.
What is the Methane Testing Process?
The LADBS Methane Test process requires onsite fieldwork for which Methane Mitigation research is necessary for preparation. The Methane Mitigation consultant must establish the methane hazard classifications per the LADBS property categorization. As a result, the Methane Hazard Classification can identify Methane Buffer Zone or Methane Zone.
Occasionally, a methane hazard zone may not exist on a property. As a result, the Methane Test process will not be necessary. Alternatively, a parcel may have a methane zone or methane buffer zone. In such cases, the property is subject to the methane testing and mitigation process. To illustrate, a list of possible Methane Hazard Classifications per the LADBS Methane Code is available below.
If a new construction project is located within a Methane Zone, the Los Angeles Department of Building and Safety will require a Methane Test.
Relative to the Methane Test results, the property will get a label as Methane Levels 1 through 5. Each Methane Level has corresponding mitigation rules. Implementation of the requirements in the Methane Mitigation Design and Construction is important.
During an LADBS Methane Test, probes go into depths of 5, 10 and 20 feet below the lowest level of the structure proposal. Once measuring Methane concentrations is complete, the top level goes to the Los Angeles Department of Building and Safety.
It is important to provide your Methane Soil Gas Survey engineer with the entire project scope. This ensures that the proper information regarding methane mitigation rules are in communication.
LADBS Site Investigation Standards for Methane Testing
The LADBS methane seepage regulations outline site investigation standards for methane. These regulations provide information bulletins, affidavits and forms which give direction regarding the LADBS methane hazard mitigation requirements.
Shallow Methane Test
Methane concentrations for the Shallow Methane Test shall be recorded with a minimum of two per site, at a rate of one sample per 10,000 SqFt.
Deep Methane Test
The location of deep gas probes are based on the results from the shallow methane test. Deep Gas Probes install where the highest concentration of methane soil gas is measured. At least one gas probe is the requirement for every 20,000 SqFt (Minimum of two gas probe sets). Two sequential measurements shall be taken, with a minimum of 24 hours between sampling of the methane probes.
Methane Testing Equipment
Catalytic methane sensors and differential pressure gauges are useful to record the methane soil gas concentrations and pressures. Sensors and gauges are calibrated prior to each field day.
Methane Zone: The Los Angeles Department of Building and Safety
If LADBS denotes an area as a possible methane hazard, the classification is likely a result of historical or existing oil drilling.


What will happen on my property during a Methane Soil Test?
LADBS requires Methane Tests according to the LADBS Methane testing standards. The testing will consist of multiple soil gas probes to monitor methane gas pressure and concentrations. The quantity and depth of these methane probes are a function of the property size and the scope of work.
Further, methane testing experts will place shallow soil gas probes at additions of one for every ten thousand square feet of property. The methane engineer place deep soil gas probes at one for every twenty-thousand square feet.
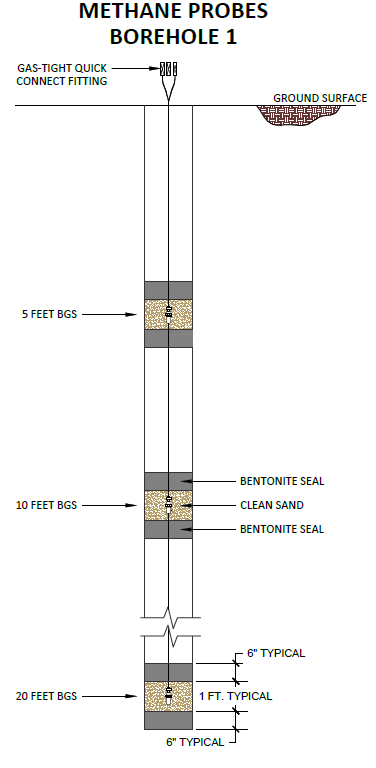
Shallow methane soil gas probes are five feet below the lowest level of the expected structure. Deep methane soil gas probes are at a depth of five, ten, and twenty feet below the lowest level of your structure.
Accordingly, properties less than twenty thousand square feet will consist of two boreholes with methane probes at five, ten, and twenty feet below the lowest level of the structure.
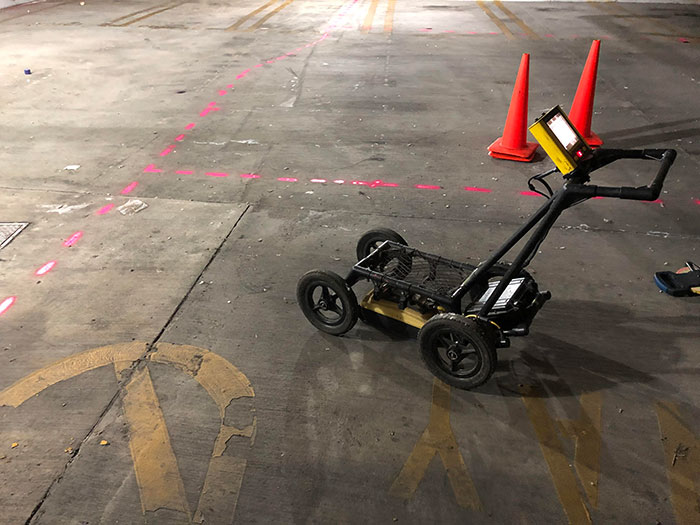
Methane Testing with Underground Utilities and Ground Penetrating Radar
Environmental field technicians identify the locations of the methane boreholes during a site survey. The methane mitigation consultant settles the scope of the Methane Testing before the Site Survey. Thereafter, engineers use their judgment to locate the boreholes in areas that will not affect underground utility lines. Subsurface utilities that may interfere with the methane boreholes are waterlines, gas lines, sewer lines, and electrical conduits. Electrical conduits can consist of low-voltage and high-voltage electricity. The borehole location will be marked using chalk paint or a semi-permanent delineation tool.
Geophysical Survey Options During Methane Mitigation Planning
Because engineering judgment is inexact, guiding ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is still required. This process holds hiring a third-party surveying specialist to scan the underfloor and verify that the expected methane test borehole locations do not conflict with any underground utilities. The ground-penetrating radar company will collaborate with DigiCert to help root and finalize any possible underground utilities present. DigAlert is a government-managed company that organizes underground utility companies’ responses to the proposed scope of work that may conflict with their utility lines. It is the law to call DigAlert if you are digging during Methane Mitigation construction within Los Angeles. Submitting a DigAlert ticket falls within the responsibility of the Methane testing specialists and Methane Mitigation Contractor.
Direct Push Drilling for Methane Soil Gas Testing
The drilling team can advance the methane testing boreholes once the GPR consultant clears all utility lines. Boreholes will be built per Methane Testing Standards by an LADBS testing laboratory and California professional engineer. Consequently, these environmental soil gas tests utilize a special drilling methodology, direct push drilling. Direct push drilling minimizes intrusive activities to the soil and sub-surface to ensure that native conditions are disturbed minimally. A drilling contractor will use special equipment to advance the direct push drilling boreholes. Direct push is a drilling method similar to hammering a rod into the soil. This puncture method is far less intrusive in comparison to rotary-style drilling methodologies.
Due to the specialty drill rig used in the process and the necessary high skill level of the drillers. A direct push drilling costs a significant amount of money. However, this drilling process causes minimal soil disruption. Thus increases the accuracy of the methane test results, ultimately sparing you from expense padding due to false results brought about by the lower-cost rotary drilling technique. Inexperienced environment engineering companies will usually utilize the rotary drilling technique to lower methane testing costs, maximizing their profit margins.
Vapor Probes installed with Direct Push Drilling
The vapor probes will place commonly within a 1-foot column of number three granulated sand. This allows for proper fluid flow during the testing. The testing is generally complete with a monitor, possibly a methane concentration monitor, CH4, and oxygen. These monitors will typically use either infrared sensors or the combustion one. Which has catalytic sensors to test and detect the minimum/maximum methane concentrations below the ground surface. This information will determine which materials will be in use for the Methane Gas Mitigation Construction. Specifically for what will be in use for the installation of Methane Barrier. The methane testing equipment must calibrate before every project to minimize the chance of error.
The column of sand where the vapor probes go is usually between Two columns of moist bentonite. Bentonite is essentially a clay that expands when moist to double the volume, which creates an excellent seal. Because this material surrounds the location of the vapor filters, it guarantees the probes sealant are tight. Then the sections place between other depths of the borehole.
Soil Gas Probe Construction
The responsible professional engineer will supervise, inspect and verify the methane testing work. The methane testing work and soil gas borehole construction must be per LADBS testing standards’ specifications. During drilling, it will be the responsibility of the drilling contractor to place the methane soil gas probes per the LADBS Testing standards. The construction of a soil gas probe consists of binding a porous vapor probe within a sand layer. And bindin the sand between two bentonite seal layers. The sand allows for a porous region to promote soil gas migration. Concurrently. Moreover, the bentonite seal will prevent soil gas seepage. Consequently, the bentonite will ensure the exact methane soil concentrations at the corresponding depth.
Methane soil gas probe construction executes based on the ASTM standards while considering the local building code and testing jurisdiction requirements. To initiate the construction, an environmental professional must first establish the underground utility markings. This is a crucial step in Methane Mitigation Construction because it is likely that the construction will cause unintentional environmental, electrical, and sewage damage. Marking all underground utilities ensures that preventative measures execute to reduce the possibility of destruction to existing underground utilities. These are usually difficult to locate due to the unpredictable utility line routings. A third-party environmental professional might be a requirement to scan the area with ground-penetrating radar. This ensures that all borehole locations are clear. In any case, it is always essential to verify with the methane testing consultant whether the underground utilities will identify and cleared or not.
Methane Soil Gas Probe Depth
After marking and clearing underground utilities, direct push drilling comes next. This process is complete using a directly push drill rig. It forces drilling probes to penetrate the soil with minimal disturbance to the surrounding areas. These drilling probes include polyethylene tubing with vapor probes connected to them. These gas vapor probes will be place at a certain depth below the ground surface. There may be one probe in a borehole, which is known as a single-nest soil gas probe. If two or more probes are to install, these are known as dual- and triple-nest soil gas probes, respectively.
Measuring Methane Concentrations During LADBS Methane Test
Methane Testing for a single-family dwelling or an accessory dwelling unit commonly consists of two boreholes. Furthermore, each borehole will have three soil gas probes five, ten, and twenty feet below the ground surface. Engineers record the Methane soil Gas measurements at the three depths of each borehole. Again, testing complies with the LADBS Methane Testing standards. Field Scientists monitor the methane soil gas and pressure concentrations during two days.
Results and Conclusions of LADBS Methane Soil Gas Testing
The LADBS Methane Testing official form is the certificate of compliance for methane test data. The certificate of compliance will outline the results of the Methane Test. LADBS will review to establish the Methane Mitigation Design and Methane Mitigation Construction requirements after reviewing the methane test results.
Certificate of Compliance for Methane Test Data
Upon completion of the Methane Test, Sway Features will prepare the Certificate of Compliance, this will include the methane concentrations and methane pressures which will categorize the final methane site design level. The certificate of compliance needs to prepared by a California licensed professional engineer.
Methane Mitigation Design
Based on the results of the Methane Test, a Methane Mitigation System designed by a Licensed Engineer and approved by the Los Angeles Department of Building and Safety will be required. The Methane Mitigation Components could include; Passive Sub-Slab Vent, Impervious Membrane, Mechanical Extraction, Gas Detection, Mechanical Ventilation, Alarms, Trench Dams, Conduit Seals, and Dewatering.
Methane Mitigation Contractors
Once a Methane Mitigation Design is acceptable by the Los Angeles Department of Building and Safety, the design implements within the construction project. The Methane Mitigation Construction completes through a specialty contractor that has license and certification to do so. During Construction, a Methane Deputy Inspector will have to oversee and approve the installation.
